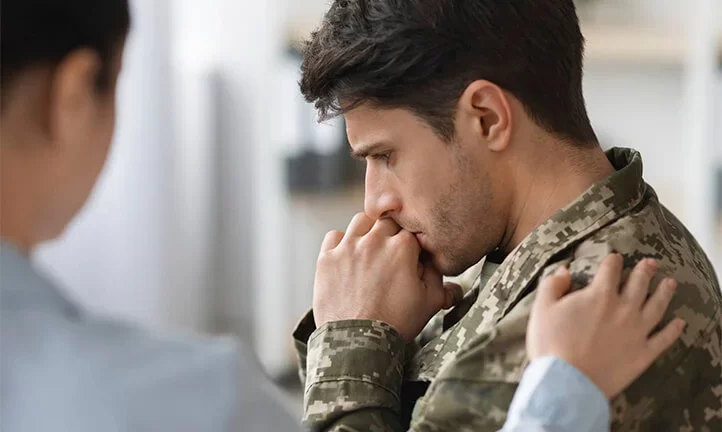
Psychological rehabilitation of military personnel is a process aimed at helping veterans effectively adapt to civilian life after war. It includes a set of techniques designed to alleviate symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, anxiety, and other psychological consequences associated with combat.
These techniques may include individual and group psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, stress management techniques, and the use of medications if necessary. The goal of psychological rehabilitation is to support military personnel on their path to recovery and help them find a new balance in civilian life.
Psychological rehabilitation of military personnel is important not only for the warriors themselves but also for their families and society as a whole, as it helps ensure a healthy and productive return of veterans to civilian life.
Additionally, the psychological rehabilitation of military personnel plays a crucial role in the process of reintegrating our defenders into society, helping them maintain a high quality of life and activity, thus reducing the social and economic costs associated with psychological disorders caused by military service.
Psychological Rehabilitation of Military Personnel: Veterans’ Issues
Military personnel often face psychological challenges, particularly post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, anxiety, and other stress-related disorders. War-related traumas, including the loss of comrades, experiencing severe combat situations, and constant danger, can lead to long-term mental stress affecting their daily lives.
Another significant issue is the adaptation to civilian life after military service. Changing environments, finding a job, and establishing relationships with family and friends can all be extremely challenging. Military personnel often face feelings of alienation, lack of purpose, and disconnection from civilian society.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is one of the most common issues faced by veterans. It is a condition that can develop after witnessing or experiencing a life-threatening traumatic event, such as combat.
Veterans with PTSD may have prolonged negative emotional, physical, and psychological reactions, including fear, persistent memories of the traumatic event, isolation, irritability, nightmares, constant alertness, and loss of interest in previously enjoyable activities. These symptoms severely interfere with daily life and social adaptation, including work, education, and personal relationships.
An essential part of psychological rehabilitation for military personnel is addressing PTSD. This may include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to help individuals change negative thoughts and reactions related to the trauma, medication therapy to alleviate some symptoms, and prolonged exposure therapy to help veterans relate less painfully to their memories. Group support, helping military personnel feel understood, is also important.
Depression and Anxiety
Depression and anxiety are two more mental health conditions and critical aspects of psychological rehabilitation that military personnel often encounter.
Depression is a condition characterized by feelings of sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in previously enjoyable activities, sleep problems, changes in appetite, fatigue, feelings of guilt or worthlessness, and difficulty concentrating. Depression can significantly impact veterans’ quality of life, their relationships, and their ability to work or study.
Anxiety refers to various disorders characterized by excessive or uncontrollable feelings of fear or worry. Military personnel with anxiety disorders often experience panic attacks, constant fear, or excessive anxiety for various reasons.
Addressing these conditions is a vital part of psychological rehabilitation for military personnel. Therapeutic assistance, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can be beneficial for veterans with depression and anxiety. Medication therapy may also be necessary during their recovery process.
Suicidal Tendencies
Suicidal tendencies are a serious issue among veterans and a crucial element in the psychological rehabilitation process for military personnel. Suicidal tendencies include thoughts of suicide, planning suicide, suicide attempts, and cases of successful suicide.
Suicide cases among military personnel are caused by several factors, including PTSD, depression, anxiety, chronic pain, sleep problems, and other mental and physical issues. Many veterans also face challenges adapting to civilian life after service, such as employment, personal relationships, and a sense of lost identity and purpose.
Professional psychologists, psychotherapists, and psychiatrists involved in the psychological rehabilitation of military personnel often use special strategies to prevent suicide and provide support. This can include cognitive-behavioral therapy, medication therapy, self-care strategies, group support, and individual therapy. The most critical task here is the early identification of suicidal tendencies and immediate response by specialists.
Readaptation to Civilian Life
Readaptation to civilian life is one of the key aspects of psychological rehabilitation for military personnel. After military actions, soldiers often face challenges related to changing their lifestyle, environment, and role in society.
- Challenges of readaptation may include the loss of identity associated with military service, employment problems, establishing relationships with family and friends, and adapting to a less structured life.
- Support during the readaptation process. Providing military personnel with appropriate resources, support programs, psychological assistance, and access to professional training can help them successfully transition to civilian life. This can include career counseling, working with a psychologist to discuss arising challenges and develop strategies to overcome them.
- The role of psychological rehabilitation. Psychological rehabilitation helps military personnel cope with mental challenges such as PTSD, depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts that may arise during the readaptation process. It also enables veterans to develop the skills necessary for a successful adjustment to civilian life.
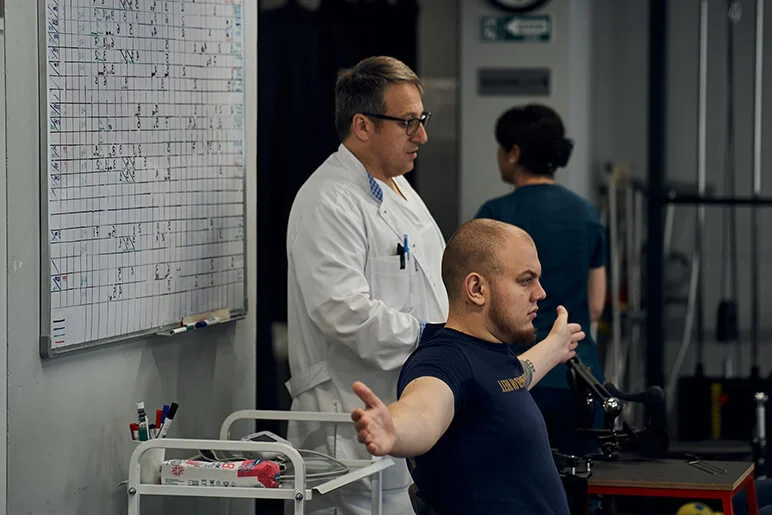

Methods of Psychological Rehabilitation for Military Personnel
Psychological rehabilitation for military personnel includes various techniques and approaches designed to ease the recovery and readaptation process to civilian life. One key method is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which helps veterans recognize and change negative patterns of thoughts and behaviors. CBT can be particularly effective in processing traumatic memories, reducing PTSD symptoms, and eliminating suicidal thoughts.
Another important method is group therapy, allowing military personnel to share their experiences and feelings in a safe and supportive environment. Support groups create a sense of community and mutual understanding, which can be very beneficial during recovery. Other techniques, such as relaxation, meditation, biofeedback, and mindfulness, are also used.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the main methods used in the psychological rehabilitation of military personnel. It is based on the principle that our thoughts (cognitions) influence our behavior and emotions. Therefore, changing negative or destructive thoughts can change behavior and improve emotional well-being.
In the context of military personnel, CBT can be particularly effective in treating stress- or trauma-related disorders, such as PTSD. The therapy aims to identify and change harmful thought patterns that have resulted from military experiences. It involves working on traumatic memories, learning self-help techniques to reduce anxiety and stress, and developing new, healthier ways to cope with negative emotions.
CBT is also effective in treating other mental disorders, such as depression or anxiety, which often occur in military personnel. It helps former soldiers understand and change thought and behavior patterns that cause or exacerbate negative symptoms.
Group Therapy
Group therapy is a crucial component of psychological rehabilitation for military personnel. It creates a safe environment where veterans can share their experiences and feelings. This not only helps soldiers feel that they are not alone in their problems but also promotes learning new ways to overcome stress and anxiety.
In group therapy, military personnel can learn from the experiences of others, receiving support and advice from those going through similar trials. They can also receive constructive feedback and recognition for their achievements in the recovery process.
Moreover, group therapy helps military personnel improve their interpersonal skills. They learn to listen to others, express their thoughts and feelings, and develop strategies for constructive conflict resolution. All this can be beneficial not only in the rehabilitation process but also in civilian life.
Virtual Reality Therapy
Virtual reality (VR) therapy is becoming increasingly common in the context of psychological rehabilitation for military personnel, especially for treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
VR therapy allows veterans to recreate and relive traumatic events in a controlled and safe environment. VR technology specialists can create realistic simulations of military scenes, helping military personnel confront traumatic memories.
During the therapy process, the military personnel feel completely safe and in control of the situation, while the therapist provides immediate support and manages the process. This contributes to the gradual reduction of the emotional impact intensity of traumatic memories.
VR therapy is also effective in teaching new stress-coping strategies, helping military personnel acquire important self-help and self-regulation skills that they can apply in everyday life.
Family Therapy
Military service impacts not only the soldiers but also their families. Therefore, family therapy is an indispensable tool in the psychological rehabilitation of military personnel. It helps all family members understand and adapt to these changes.
In the context of military families, therapy is often focused on issues such as the transition of military personnel to civilian life, overcoming stress or psychological trauma, and providing support to the soldier’s family, which may also face stress or anxiety.
Family therapy involves various methods and techniques aimed at improving mutual understanding and empathy between family members, helping them better support each other during the rehabilitation process of the military personnel.
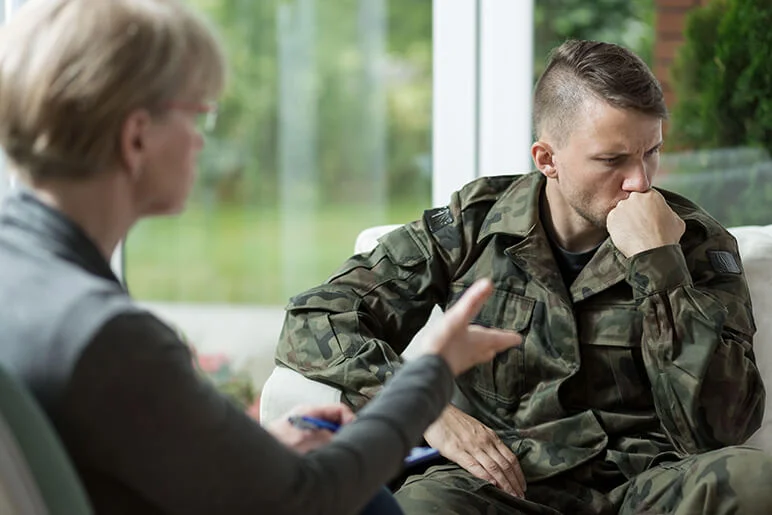

The Role of Various Participants in the Rehabilitation Process of Military Personnel
The psychological rehabilitation process of military personnel involves various participants, each playing a crucial role—from the servicemember themselves to healthcare professionals, family members, and society. The servicemember, as the main participant, needs to be actively engaged in the rehabilitation process, participating in decision-making and being motivated towards recovery.
Healthcare professionals, including psychologists, psychiatrists, social workers, and other therapists, play a key role in providing specialized assistance, defining rehabilitation strategies, and monitoring their effectiveness.
Family members and close friends also play an essential role by providing emotional support and helping the servicemember adapt to everyday life. Lastly, society can provide resources and support to facilitate successful rehabilitation, including employment services, support groups, educational programs, and more.
The Role of Psychologists
Psychologists play a significant role in the psychological rehabilitation of military personnel, performing a range of key tasks and utilizing their unique skills and knowledge.
- Diagnosis and Assessment: Psychologists use their expertise to identify psychological issues such as PTSD, anxiety, depression, and suicidal tendencies, develop individual rehabilitation plans, and assess their effectiveness.
- Conducting Therapy: Psychologists employ various therapeutic techniques, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), group therapy, family therapy, and innovative methods like VR therapy, to help servicemembers counteract negative psychological impacts.
- Consultation and Mentorship: Psychologists assist servicemembers and their families in understanding and dealing with psychological challenges related to war and reintegration into civilian life.
- Research and Education: Many psychologists are involved in research, studying the effectiveness of different rehabilitation methods and exploring the specifics of military psychological issues. They develop new strategies and tools to overcome trauma and stress caused by military service. Psychologists also engage in educational activities, training new professionals in the field of rehabilitation and raising awareness about the psychological consequences of combat.
- Community Work: Psychologists often collaborate with other organizations and services supporting servicemembers, such as employment services, charitable organizations, educational institutions, and more. They provide consultations, conduct training, and offer other support to help these organizations better meet the needs of military personnel.
- Advocacy and Policy Implementation: Psychologists work at higher levels to help shape and implement policies that improve support for servicemembers and their families. They collaborate with government agencies and international organizations to advocate for greater understanding and support for military personnel.
- Collaboration with Medical Staff: Psychologists often work in teams with medical professionals such as psychiatrists and nurses to provide comprehensive care for servicemembers. They help coordinate care and support, often acting as intermediaries between servicemembers, their families, and medical staff.
- Aid in Readaptation: Psychologists assist servicemembers in navigating the readaptation process to civilian life after service. They work with warriors to help them understand and overcome challenges related to the transition period, including overcoming psychological trauma, developing new skills, and finding new directions in life.
The Role of Family and Close Ones
Family and close ones play a critically important role in the psychological rehabilitation process of military personnel.
- Support and Understanding: Family is an important source of emotional support. Understanding and support from close ones can significantly enhance the sense of security and help servicemembers better cope with negative emotions.
- Participation in the Therapeutic Process: Families are often involved in the therapy process. They may be included in family therapy sessions, where they learn to better understand and respond to the needs of the servicemember.
- Role in Reintegration: Through structured everyday life, routine, and stability, family can help servicemembers reintegrate into civilian life more quickly.
- Assistance in Daily Life: Family can also provide practical help, such as managing household chores, performing daily tasks, and organizing medical care.
- Support in Stress Management: Family and close ones can help servicemembers manage stress by providing emotional support and promoting healthy ways of relaxation and recovery.
- Social Support: Family can support servicemembers in expanding their social networks and resources, helping them connect with support groups, veteran specialists, or other community organizations.
- Adapting to Changes: Family can help former military personnel adapt to changes in their physical or mental health, manage emotions, and adjust expectations.
- Help with Suicidal Thoughts: Family and close ones can offer vital support to servicemembers experiencing suicidal thoughts by providing immediate help and ensuring access to professional psychological counseling.
- Support in Rehabilitation: Family can be a significant factor in the successful rehabilitation process, helping servicemembers apply new strategies and skills learned in therapy to everyday life.
- Strengthening Resilience Factors: Family can assist servicemembers in strengthening resilience factors such as self-belief, optimism, self-help strategies, and social support, which are important for their psychological rehabilitation.
The Role of the Military Community
The military community plays a significant role in the psychological rehabilitation process of military personnel.
- Support Community: Military comrades form the backbone of the support network for veterans. They can share their own experiences, offer advice, and help combat isolation and a sense of alienation.
- Understanding and Empathy: Members of the military community, having shared service experiences, better understand the difficulties veterans face. Their empathy and understanding are extremely valuable in the recovery process.
- Group Therapy: Participation in group therapy with other former military personnel can be an effective means of learning new problem-solving strategies.
- Mentorship: Experienced veterans who have successfully gone through rehabilitation can act as mentors for those just beginning this process.
- Advocacy: The military community can assist in advocating for veteran interests, promoting policies in healthcare, employment, education, etc.
- Contribution to Research: Due to their unique perspective and experience, the military community can make important contributions to research aimed at developing and improving psychological rehabilitation methods for military personnel. Their experience and deep understanding of veteran issues enable the development of more effective rehabilitation programs and improvements in support practices.
- Overcoming Barriers: The military community can help veterans overcome the stigma associated with seeking psychological help and assist them in better understanding and expressing their emotions and needs.
- Rehabilitation Assistance: Members of the military community can assist servicemembers in learning and applying new rehabilitation strategies and skills.
- Developing Responsibility: The military community can help servicemembers develop a sense of responsibility for their own health and well-being, which is an important step in the rehabilitation process.
- Expanding Social Networks: The military community can help servicemembers expand their social networks, which will contribute to their psychological recovery and integration into civilian life.

Prospects for the Development of Psychological Rehabilitation for Military Personnel
Researchers and practitioners in the field of psychological rehabilitation are continually refining methods and techniques for working with military personnel. This includes the development of new forms of group and individual therapy, the implementation of humanistic approaches focused on individual needs, and the creation of comprehensive programs that encompass not only psychological but also social and professional rehabilitation.
Additionally, research aimed at evaluating the effectiveness of various rehabilitation methods is progressing, which contributes to their ongoing improvement.
Implementation of New Technologies
The integration of new technologies into the psychological rehabilitation of military personnel is becoming an increasingly important aspect of modern practice. This encompasses a wide range of innovations, from virtual reality to augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
- Virtual Reality (VR) is already being used to create a controlled, safe environment where servicemembers can relive and process traumatic experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning can be utilized to analyze psychological metrics and predict the psychological support needs of servicemembers.
- Mobile Applications and Telemedicine enable continuous support, including health monitoring, online psychological consultations, informational resources, and self-help techniques.
- Video Games and Gamification help engage servicemembers in the rehabilitation process, making it more interesting and less stressful.
These and other technologies are already transforming the landscape of psychological rehabilitation, offering new possibilities for supporting servicemembers in their recovery and transition to civilian life.
Advancing Scientific Research in Psychological Rehabilitation of Military Personnel
The advancement of scientific research in this field is critical for maintaining effectiveness and continuous improvement. This involves not only studying new treatment methods but also understanding the complex psychological challenges faced by military personnel.
- Therapy Effectiveness: By researching the effectiveness of various therapy formats, scientists can identify which methods best help servicemembers overcome psychological trauma.
- Psychological Health Support: Research focuses on the mental health of servicemembers, examining how war, combat, and military service impact mental health and ways to support it.
- Transition to Civilian Life: Studies also focus on the challenges of transitioning to civilian life, exploring how to best influence this process.
- Prevention: Beyond working with servicemembers already suffering from mental disorders, research also aims at prevention, seeking ways to reduce the risk of such issues in the future.
Changing the Social Stigma Associated with the Mental Health of Military Personnel
Changing negative societal associations with mental health is a key element in supporting military personnel. Society must better understand the mental health issues veterans face so they can seek help without fear or shame.
This means promoting the understanding that mental health problems such as PTSD, depression, and anxiety are real and significant issues that require professional treatment. Additionally, it’s important to change the narrative that mental health issues are a sign of weakness.
Conversations about mental health need to become the norm, especially in military environments. Empathy, understanding, and continuous societal support can greatly contribute to the successful psychological rehabilitation of military personnel.




