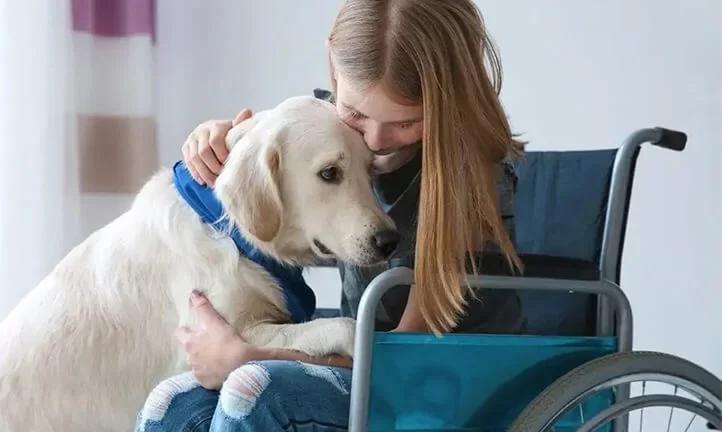
Animal-assisted therapy (zootherapy or pet therapy) is a type of therapy that involves interactions between patients and animals to improve overall human health and alleviate symptoms of various diseases. It is an interdisciplinary approach that combines elements of psychology, veterinary medicine, and social work.
The goal of animal-assisted therapy is to help people cope with various issues: physical, psychological, emotional, or social, including stress relief, combating depression, improving motor skills, social interaction, self-esteem, and overall well-being.
Methods of animal-assisted therapy are diverse and depend on the specific treatment goal. It can involve simple interactions with animals, taking care of them, training, or even performing specific exercises together. Depending on the particular case, different types of animals are used in animal-assisted therapy, from pets (such as dogs and cats) to horses and dolphins.

History of Animal-Assisted Therapy
Animal-assisted therapy, although it may seem like a modern method, actually has a long history. The use of animals for healing and improving well-being can be traced back to various cultures over many centuries.
In ancient civilizations such as Greece, Rome, and Egypt, animals played an important role in religious and healing rituals. For example, in Ancient Egypt, cats were considered sacred animals and were used in healing rituals.
The first mentions of therapy involving animals in a medical context date back to the 18th century when asylums in England allowed patients to interact with animals in a controlled environment to improve their mental state.
Modern zootherapy began to develop in the 1960s, mainly due to the work of American psychologist Boris Levinson, who found that patients, especially children, responded better to therapy when his own pets were present. These observations led to further research and the formalization of animal-assisted therapy as a recognized treatment method.
Today, animal-assisted therapy is used in many fields, including psychiatry, psychology, psychotherapy, pedagogy, and psychological rehabilitation. It is recognized by many medical and psychological communities as an effective method of supporting health and well-being.

Methods and Approaches in Animal-Assisted Therapy
Animal-assisted therapy encompasses a variety of methods and approaches that use human-animal interaction to improve physical, psychological, or social well-being. Methods vary depending on the specific therapy goal, type of animal, and patient needs. The main approaches include direct interaction with animals (such as petting, feeding, playing) and observing them.
These approaches are applied in various situations: from individual sessions to group activities, from working with children to assisting the elderly. They are also adapted to the specific needs of patients, for example, in the case of people with autism, post-traumatic stress disorder, depression, and other conditions. The primary goal is always to promote the improvement of the patient’s quality of life and well-being.
Overview of Main Techniques in Animal-Assisted Therapy
- Dog Therapy: Dogs are among the most commonly used animals in animal-assisted therapy. They help increase physical activity, improve social skills, and enhance the overall emotional state of patients. Dog therapy is used to help children with autism, patients with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), the elderly, and many others.
- Horse Therapy (Equine Therapy): Horses are often used in therapy to help people with physical and emotional issues. Equine therapy helps improve balance and coordination, strengthen muscles, develop social skills, and boost self-esteem.
- Cat Therapy: Cats are commonly used in animal-assisted therapy to create a calming and relaxing atmosphere. They are particularly beneficial for people with depression or anxiety.
- Dolphin Therapy: Although this technique is more specialized and requires specific conditions, it is beneficial for children with various psychological and physical disorders, including autism and cerebral palsy.
- Bird and Small Animal Therapy: Birds, rodents, rabbits, and other small animals are also used in animal-assisted therapy. They help improve motor skills, increase concentration levels, and enhance overall emotional well-being.
These are just a few examples of methods and techniques in animal-assisted therapy. The key to this process is an individual approach that considers the unique needs and goals of each patient.

Which Animals Are Used for Treatment in Animal-Assisted Therapy?
Various types of animals are used in animal-assisted therapy, with the choice depending on the therapy goals, patient preferences, availability, and the capabilities of the specific setting. Here are some examples:
- Dogs are among the most common therapeutic animals due to their empathy, trainability, and ability to interact with people. They help with social skills training, stress and anxiety reduction, improved physical activity, and self-esteem.
- Cats are typically chosen to create a calming and relaxing environment. They help improve mood and relieve stress.
- Horses have unique characteristics that allow them to learn and respond to human emotions, making them ideal for working with people who have emotional and psychological issues. They also help improve coordination and balance.
- Dolphins: Interaction with dolphins improves motor skills, social abilities, and emotional state.
- Birds and Small Animals: Birds, rodents, and rabbits help improve motor skills, increase concentration levels, and enhance overall emotional well-being.
- Fish: Observing fish in an aquarium acts as a relaxing and meditative stimulus, reducing stress and anxiety levels.
The choice of a specific animal depends on many factors, including the patient’s specific needs, the presence of allergies, and the therapy’s feasibility and conditions.

Can Animal-Assisted Therapy Replace Traditional Treatment?
Animal-assisted therapy does not oppose traditional treatment but complements it, working in symbiosis with more standard approaches. While traditional treatment focuses on medication and psychotherapy, animal-assisted therapy offers an alternative or additional approach, using interaction with animals as a therapeutic tool.
This therapy is especially useful in cases where patients cannot or do not want to take medications, or when standard treatment methods do not produce the expected results. Animal-assisted therapy can also improve patients’ quality of life by reducing stress levels, improving mood, and providing positive social interaction. However, it is important to note that pet therapy should be conducted by professionals and adequately integrated into the overall treatment plan.
Comparison of Animal-Assisted Therapy and Traditional Treatment: Advantages and Disadvantages
Animal-assisted therapy and traditional treatment have their unique advantages, serving different patient needs. Zootherapy, based on interaction with animals, helps reduce stress and anxiety levels, improve mood, and foster socialization. However, it has some limitations, such as allergies in some patients and accessibility issues in certain locations.
Traditional treatment, on the other hand, is a well-researched and widely applied approach with many specialized facilities and professionals. However, it can cause side effects from medications and stress from medical procedures.
Nevertheless, both approaches are often used together to achieve the best results.
Animal-Assisted Therapy
Advantages:
- Holistic Approach: Animal-assisted therapy cares for the patient’s physical, emotional, and social well-being, while traditional treatment focuses more on the physiological aspect.
- Low Stress Levels: Interaction with animals is usually low-stress, improving mood, reducing anxiety, and enhancing overall well-being.
- Improved Social Skills: Animals can help improve social skills and communication, especially for children and people with certain mental disorders.
Disadvantages:
- Risk of Allergies: Some people may have allergies to animals, limiting their ability to participate in animal-assisted therapy.
- Accessibility: Not all medical facilities can offer zootherapy services, creating access issues for some patients.
Traditional Treatment
Advantages:
- Extensive Research: Traditional treatment methods are supported by extensive research and included in clinical guidelines.
- Specialized Care: Doctors and other healthcare professionals are trained in specialized care and treatment.
Disadvantages:
- Side Effects: Some medications cause side effects, which can worsen the patient’s overall condition.
- Stress from Medical Intervention: Many procedures can cause anxiety or fear in patients.
It is important to remember that animal-assisted therapy and traditional treatment do not exclude each other, and often the best results can be achieved by combining both approaches in an individually developed treatment plan.
Examples of Cases Where Animal-Assisted Therapy Was More Effective
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Military veterans and others who have experienced traumatic events often face PTSD. Studies show that animal-assisted therapy, especially with dogs, can significantly help reduce PTSD symptoms, improve social interaction, and decrease the use of medical services.
- Autism: For children with autism spectrum disorders, social interaction can be challenging. Dogs and other animals help children with autism improve social skills and establish communication with others.
- Dementia: Patients with dementia often suffer from anxiety, stress, and depression. Animal-assisted therapy helps improve the quality of life for these patients by reducing anxiety and enhancing social interaction.
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Studies show that regular interaction with animals helps reduce aggression and anxiety, often associated with some stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Depression and Anxiety: Animals help people cope with depression and anxiety by providing emotional support and creating a sense of calm.

Indications and Contraindications for Animal-Assisted Therapy
Animal-assisted therapy (AAT) is indicated for a wide range of conditions and problems. It can be beneficial for people suffering from mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and autism. AAT is also frequently used to help people with cognitive impairments, including dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, it is useful for those experiencing pain or stress associated with chronic illnesses or long-term recovery from injury or surgery.
However, AAT also has contraindications. People with allergies to animals or a fear of them are not suitable candidates for this type of therapy. Moreover, if a patient has an immunodeficiency or is recovering from surgery, animal-assisted therapy is not recommended due to the risk of infection.
Diseases and Conditions for Which Animal-Assisted Therapy is Beneficial
Pet therapy has a wide range of applications and can be beneficial for treating many diseases and conditions. Here are some examples:
- Mental Disorders: AAT is often used as an adjunct to traditional treatments for mental illnesses, including depression, anxiety, PTSD, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. Interaction with animals helps reduce symptoms of these disorders and improve overall well-being.
- Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD): For children and adults with ASD, AAT helps improve social skills, promotes emotional learning, and reduces stress and anxiety.
- Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: AAT can improve the quality of life for patients with dementia or Alzheimer’s by reducing aggression, anxiety, and depression.
- Chronic Pain: AAT is also beneficial for people suffering from chronic pain, such as fibromyalgia or chronic spinal pain syndrome. Interaction with animals helps reduce pain sensations and improve overall well-being.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Research shows that interaction with animals helps lower blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall stress, which is very important for people with cardiovascular diseases.
- Recovery After Injury or Surgery: AAT is a useful part of the recovery program after injury or surgery, helping patients cope with pain, stress, and anxiety related to their condition.
Potential Risks and Limitations of Animal-Assisted Therapy
Despite numerous potential benefits, AAT is not without risks and limitations that should be considered.
- Allergies: Some people are allergic to animals, which can cause serious health problems, including asthma, skin rashes, and even anaphylactic shock.
- Bites and Scratches: Although animals used in therapy are typically carefully selected and trained, there is always a risk of bites or scratches, especially if a patient accidentally provokes the animal.
- Fear of Animals: Some people may have a fear of animals (zoophobia), making AAT ineffective or even counterproductive for them.
- Infectious Diseases: Animals can carry bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can be transmitted to humans. While such cases are rare, they are dangerous, especially for people with weakened immune systems.
- Long-term Effectiveness: Despite positive results in short-term studies, the long-term effectiveness of AAT is not yet fully understood. More longitudinal studies are needed to fully understand its healing qualities.
- Limited Access: Unfortunately, many medical facilities have limited access to AAT due to a lack of trained animals or certified therapists.

Scientific Research in the Field of Animal-Assisted Therapy
Scientific research in this field continues to expand and provides confirmation of many of its benefits. Studies indicate improved mental health in people suffering from depression and anxiety through interaction with animals, as well as confirm reduced stress and blood pressure, improved overall well-being, and social interaction in patients with various diseases and disorders, including dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and autism spectrum disorders.
However, many of these studies do not always meet the standards of randomized controlled trials. This necessitates more extensive, long-term research to fully understand the effectiveness of AAT and confirm its long-term benefits.
Review of Studies Confirming the Effectiveness of Animal-Assisted Therapy
- A 2017 study conducted at the Royal Children’s Hospital in Britain showed that the use of pet therapy helped reduce children’s fear before surgery and decreased pain after surgical intervention.
- A 2016 study published in “BMC Psychiatry” found that patients with schizophrenia who participated in pet therapy improved their overall mental state and reduced their stress levels.
- A study published in 2019 in the “Journal of Pediatric Oncology Nursing” showed that children with cancer who participated in AAT improved their emotional state and quality of life.
- A 2020 study published in the “American Journal of Men’s Health” showed that AAT helps improve the mental health of men undergoing treatment for alcohol or drug addiction.
It is important to note that most of these studies are based on small samples, so additional research is needed for a more thorough assessment of the effectiveness of AAT.

Conclusions and Summary
Animal-assisted therapy has a noticeable impact on patients with various conditions, including depression, anxiety disorders, PTSD, and even conditions such as autism or dementia. Modern research continues to confirm the effectiveness of this approach and indicates that it can complement or even replace some traditional treatments.
Although AAT can be more effective in some cases, it is certainly not a “cure-all.” Like any other form of therapy, it has its limitations. Moreover, it is always necessary to consider the possible risks associated with contact with animals, including allergies and the possibility of bites or scratches.
Nevertheless, given all the benefits it offers, AAT certainly occupies an important place in the arsenal of modern medical and psychological techniques. Furthermore, it can become a bridge that helps bridge the gap between traditional medicine and more humanistic, centered approaches to treatment and health care.
Animal-assisted therapy continues to strengthen its presence in healthcare, being recognized as an important alternative or complement to traditional treatments. Its integration into hospitals, clinics, and rehabilitation centers demonstrates the acceptance and perception of this therapy as an effective means of supporting the physical and emotional health of patients.
Progressive development of technology and scientific research promises new opportunities for AAT. A deeper understanding of the interaction between humans and animals, as well as the mechanisms by which pet therapy has a positive impact, may open doors to the creation of new treatment methods and approaches in AAT.
It is also impossible to exclude the potential of pet therapy as a tool for treating new mental illnesses and disorders that may arise in connection with a rapidly changing world.
Overall, the future of animal-assisted therapy looks promising. Given the increasingly widespread recognition of its benefits, as well as ongoing scientific research in this area, it is likely to become an important part of integrative medicine.