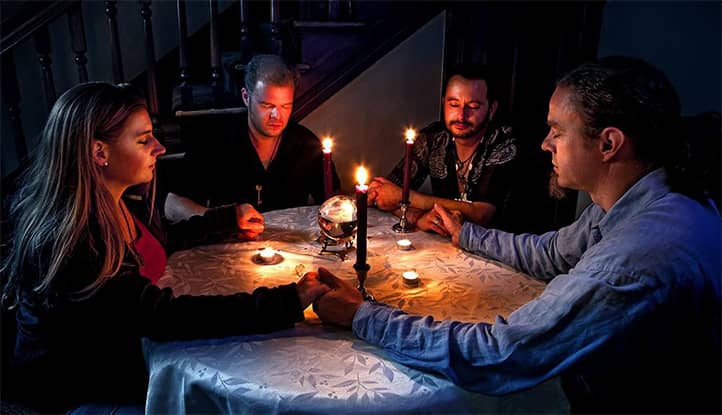
Spiritualism is a unique phenomenon that combines belief in the afterlife and the possibility of communicating with the spirits of the deceased through mediums. At first glance, it may seem like something out of the realm of mysticism or esotericism, but in reality, spiritualism has deep historical roots and remains relevant in the modern world.
Emerging in the mid-19th century, it quickly gained popularity, especially in Europe and America, where séances became not only a means of connecting with the otherworldly but also a fashionable social phenomenon. People gathered in dimly lit rooms to receive messages from deceased relatives or famous figures through mediums. This was a time when science and technology were rapidly advancing, but questions about life after death remained unanswered, creating fertile ground for the spread of spiritualism.
Today, despite advancements in science and technology, interest in spiritualism has not waned. Why? Perhaps the reason lies in the eternal human desire to find answers to questions that lie beyond our understanding. Death is one of the greatest mysteries, and the idea that life does not end with the last breath brings comfort to many.
People experiencing loss often turn to séances in the hope of receiving confirmation that their loved ones are “somewhere nearby.” Moreover, in the age of digital technology and social media, spiritualism has taken on a new form: online mediums, videos with “evidence” of the existence of spirits, and forums where people share their experiences.
But spiritualism is not just a matter of faith or comfort. It is also a phenomenon closely tied to psychology. Why do people believe in the possibility of communicating with spirits? How do séances work from a psychological perspective? And what mechanisms underlie this phenomenon? These questions make spiritualism not only fascinating but also an important subject of study.
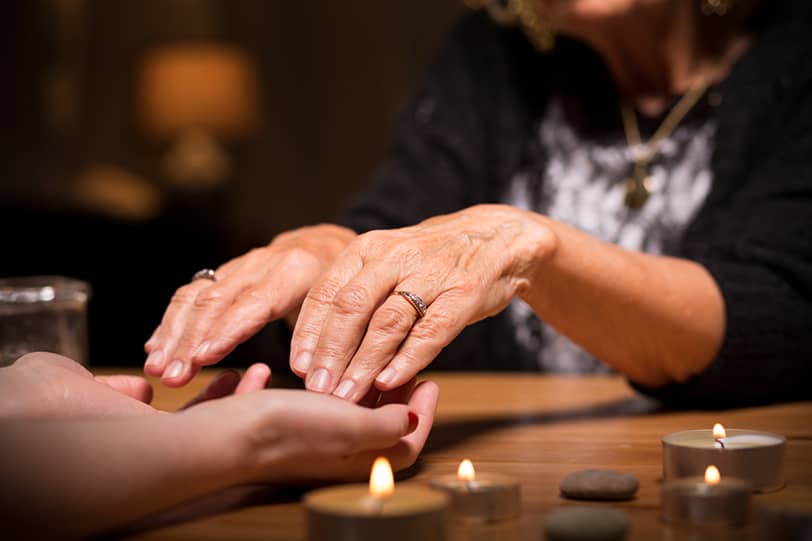

The Psychology of Belief in the Afterlife
Spiritualism, as one manifestation of belief in the afterlife, offers people not only hope for life after death but also the possibility of connecting with those who have passed on. However, behind this belief lie deep psychological mechanisms that influence our perception of reality. Let’s explore why people believe in life after death and the role mediums play in this.
Why Do People Believe in Life After Death?
One of the main reasons for belief in the afterlife is the fear of death. For many, the thought that life is finite causes anxiety and even panic. This is a natural reaction, as death represents the unknown, and the human brain struggles with uncertainty. The belief that death is not an end but a transition to another state helps people cope with this fear. It offers hope that we do not simply vanish but continue to exist in another form.
Additionally, belief in the afterlife serves as a powerful source of comfort for those grieving the loss of loved ones. The idea that deceased relatives or friends can communicate with us through mediums helps alleviate grief. This is especially important in cases where death occurs suddenly or tragically, leaving a sense of unfinished business.
Cultural and Religious Influences
Belief in life after death is also closely tied to cultural and religious traditions. Virtually all world religions—from Christianity and Islam to Buddhism and Hinduism—offer their own interpretations of the afterlife. These ideas are passed down through generations, shaping people’s worldviews. For example, in Christianity, belief in resurrection and eternal life is a fundamental tenet, while in Buddhism, the concept of reincarnation suggests that the soul continues to exist in new forms.
Cultural norms also play a significant role. In some societies, spiritual practices and communication with spirits are considered normal, while in others, they are met with skepticism. For instance, in Latin American or African countries, spiritualism is often integrated into daily life, whereas in more secular societies, it may be viewed as marginal.
Cognitive Biases
From a psychological perspective, belief in the afterlife can be explained through cognitive biases – patterns of thinking that lead us to seek meaning and patterns even where none exist.
Moreover, people tend to seek confirmation of their beliefs while ignoring information that contradicts them. This phenomenon is known as “confirmation bias.” If someone believes in the existence of spirits, they will pay attention to “signs” and “messages” that confirm their belief while disregarding rational explanations.
The Role of Mediums in Spiritualism
Mediums are individuals who claim to be able to establish contact with the spirits of the deceased. They position themselves as intermediaries between the world of the living and the world of the dead, offering their clients the opportunity to receive messages from departed loved ones. Mediums often use various techniques, such as trance states, automatic writing, or visualization, to “capture” messages from spirits.
Psychological Profile of People Prone to Mediumship
People who become mediums often possess certain psychological traits. For example, they may be more empathetic and sensitive to the emotions of others, which helps them “read” the moods of séance participants. Additionally, many mediums have a tendency toward fantasy and a rich imagination, enabling them to create vivid images and stories.
Some researchers also note that mediums may experience states of detachment or altered consciousness, where their perception seems to “separate” from reality, allowing them to feel a connection to the otherworldly. This may be due to innate psychological characteristics or training that mediums undergo to develop their abilities.
Thus, belief in the afterlife and the role of mediums in spiritualism are closely tied to psychological processes that shape our perception of reality. Understanding these mechanisms helps not only explain why people believe in spirits but also sheds light on how this belief influences their lives and emotional well-being.

Psychological Mechanisms of Séances
Séances are not just mystical rituals but complex psychological processes that immerse participants in a unique experience. At first glance, such sessions may seem magical or supernatural, but in reality, they are based on explainable mechanisms of the human psyche. The atmosphere of mystery, the emotional involvement of participants, and the skill of mediums create conditions under which people begin to believe in the reality of what is happening.
Why are participants of séances so easily suggestible? How do mediums manage to “guess” personal details about people’s lives? And why do emotions play a key role in fostering belief in the authenticity of contact with spirits? To answer these questions, it is necessary to examine the main psychological mechanisms at work during séances.
The Phenomenon of Collective Suggestion
The atmosphere of a séance plays a crucial role in shaping participants’ perceptions. Typically, such sessions are held in dimly lit rooms, with candles or soft lighting, creating a sense of mystery and detachment from everyday reality. This environment makes participants more suggestible and open to unusual experiences.
Additionally, mediums often use rituals such as burning incense, chanting mantras, or specific hand movements to enhance the effect. These actions create a sense of sacredness, further increasing participants’ trust in the proceedings.
The Placebo Effect and the Expectation of a “Miracle”
The expectation of a miracle is another powerful psychological mechanism at work during séances. If a person attends a séance hoping to receive a message from a deceased loved one, their brain begins to seek confirmation of this hope. This phenomenon is known as the placebo effect: if a person believes something is supposed to happen, their psyche starts interpreting even minor events as confirmation of that belief.
For example, a random creak of the floor or a draft of air may be perceived as signs of a spirit’s presence. Mediums often use such moments to enhance the effect and convince participants of the reality of contact with the otherworldly.
Subconscious Signals and Interpretations
The human brain is wired to constantly seek patterns and meaning, even in random events. This feature underlies many psychological phenomena that are actively utilized during séances. Mediums, often unconsciously, rely on people’s ability to interpret ambiguous signals as something significant. But how exactly does this work? And why do séance participants so readily accept general statements as personal messages?
Cold Reading
Cold reading is a technique often used by mediums to create the illusion of communication with spirits. It involves making general statements that can be interpreted as personal messages. For example, the phrase “I sense the presence of a woman who was close to you” could refer to a mother, grandmother, or sister.
Mediums also carefully observe participants’ reactions to refine their “messages.” For instance, if a person flinches or changes their facial expression, the medium may conclude that they have “hit the mark” and develop the topic further.
The Barnum Effect
The Barnum Effect is a psychological phenomenon in which people tend to accept general and vague statements as accurate descriptions of their personality or life. This effect is actively used during séances. For example, the phrase “you are going through a difficult period, but things will soon improve” can apply to almost anyone, as most people periodically face challenges.
Participants often interpret such statements as deeply personal messages from spirits, reinforcing their belief in the authenticity of the experience.
Emotional Involvement
Emotions are a powerful force that can influence our perception of reality and decision-making. During séances, the emotional involvement of participants plays a key role, transforming ordinary words and actions into something deeply personal and meaningful.
When a person experiences strong emotions, their rational thinking takes a back seat, paving the way for belief and suggestion. But how exactly do emotions shape our willingness to believe in the inexplicable?
How Grief and the Desire for Comfort Influence Perception?
Emotions play a central role in the perception of séances. People who are grieving are often in a state of emotional vulnerability. They seek comfort and hope to reconnect, even briefly, with a deceased loved one.
In such a state, a person becomes more susceptible to suggestion and is more likely to believe that the medium is genuinely communicating with a spirit. Even if the message seems dubious, the emotional need for comfort outweighs rational doubts.
The Role of Emotions in Fostering Belief in the Authenticity of Spirit Contact
Emotions not only increase suggestibility but also foster a lasting belief in the authenticity of spirit contact. When a person experiences strong feelings—whether joy, relief, or even fear—their brain remembers the experience as significant. Later, they may interpret this experience as proof of the existence of the otherworldly.
Moreover, emotions encourage séance participants to share their experiences with others, reinforcing collective belief in the reality of spiritual practices.

A Scientific Perspective on Séances
Despite their popularity and emotional appeal, séances often face criticism from the scientific community. Scientists, psychologists, and skeptics question whether there is any real evidence for the existence of spirits or if everything that occurs during such sessions can be explained using established scientific principles. The scientific approach to spiritualism involves a thorough examination of phenomena that appear supernatural and the search for rational explanations.
Criticism of Spiritualism
One of the main arguments against spiritualism is the lack of reliable scientific evidence for the existence of spirits. Despite numerous claims by mediums and séance participants, none of these assertions have been confirmed under controlled scientific conditions. Scientists have repeatedly conducted experiments attempting to document evidence of communication with the otherworldly, but all such attempts have been unsuccessful.
For example, during investigations in the early 20th century, famous mediums such as Eusapia Palladino and Mina Crandon were exposed as frauds. Their “abilities” turned out to be the result of sleight of hand and the use of hidden devices. Modern research has also failed to find evidence of spirits, casting doubt on the very foundation of spiritualism.
Examples of Exposed Mediums and Fraud
The history of spiritualism is full of examples of mediums being exposed as frauds. One of the most famous cases is the exposure of the Fox sisters, who are considered the founders of modern spiritualism. In 1888, one of the sisters confessed that all their “contacts with spirits” were the result of clever tricks, such as cracking their toe joints.
In the 20th century, mediums like Daniel Dunglas Home and Doris Stokes were also caught using cold reading and other techniques that created the illusion of communication with spirits. These cases demonstrate that the “abilities” of mediums are based on deception and manipulation rather than a genuine connection with the otherworldly.
Alternative Explanations
Many phenomena that occur during séances can be explained through psychology. For instance, hallucinations—the perception of something that does not exist in reality—can arise under the influence of stress, fatigue, or emotional tension. Séance participants, in a heightened state of suggestibility, may “see” or “hear” things that are actually products of their imagination.
Hypnosis and self-suggestion also play a significant role. Mediums often create an atmosphere that makes participants more susceptible to suggestion. In such a state, a person may interpret random sounds or movements as signs of spirit presence.
Social and Cultural Factors Supporting Belief in Spiritualism
Belief in spiritualism is also reinforced by social and cultural factors. In some cultures, spiritual practices are part of traditions passed down through generations. For example, in Latin American countries, spiritualism is often integrated into religious practices such as Santería or Candomblé.
Additionally, spiritualism often becomes a way to cope with collective traumas, such as wars or epidemics. During such times, people are particularly in need of comfort and hope that their loved ones are “somewhere nearby.” Social approval and support from others also strengthen belief in spiritual practices.

The Impact of Séances on Mental Health
Despite their controversial nature, séances have a significant impact on the mental health of participants. For some, they become a source of comfort and hope, helping them cope with difficult life situations. For others, they can lead to emotional dependency or even trauma. The influence of such practices on mental health can be both positive and negative, and it is important to understand the mechanisms underlying these effects.
On one hand, séances offer people the opportunity to “connect” with deceased loved ones, which can bring relief and a sense of closure. On the other hand, such practices often come with risks, such as manipulation and the exploitation of emotionally vulnerable individuals.
Positive Aspects
One of the main positive aspects of séances is their ability to provide comfort to those grieving a loss. For those who have lost loved ones, the idea that the deceased are “somewhere nearby” and can communicate through mediums becomes a powerful source of solace. This is especially important in cases where death occurred suddenly or tragically, leaving a sense of unfinished business.
During séances, participants often receive messages that they interpret as words of support or farewell from the deceased. This can help them process their grief, achieve closure, and move forward. For many, such experiences become an important step in the grieving process.
Reducing the Fear of Death Through Belief in an Afterlife
The belief in an afterlife, which séances reinforce, also helps reduce the fear of death. The idea that death is not an end but a transition to another state makes it less frightening. For many, this becomes a way to reconcile with their own mortality and find meaning in the finiteness of life.
Additionally, séances create a sense of connection to something greater than our everyday reality. This feeling of transcending the mundane can bring comfort and inspiration, especially to those seeking answers to existential questions.
Negative Aspects
One of the main risks of participating in séances is the potential for developing emotional dependency on mediums. People who are grieving or emotionally vulnerable may begin to rely on mediums as their sole source of hope.
Such dependency can lead to individuals constantly seeking new séances, spending time, money, and emotional resources. In some cases, this can slow down the grieving process and prevent individuals from accepting the reality of their loss.
The Risk of Manipulation and Exploitation of Vulnerable Individuals
Séances are also associated with the risk of manipulation and exploitation. Mediums may exploit the emotional vulnerability of participants for personal gain. For example, they may deliberately prolong sessions, offer additional services for money, or even extort funds under the guise of “helping the spirits.”
Moreover, some mediums may use information obtained from participants to manipulate them. For instance, they might threaten “the wrath of spirits” or promise “blessings” in exchange for certain actions. Such practices can cause serious harm to participants’ mental health, especially if they are already experiencing stress or depression.

Conclusion
Spiritualism is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that combines belief, emotions, and deep psychological mechanisms. On one hand, it offers people hope for a connection with departed loved ones, helping them cope with grief and the fear of death. On the other hand, such practices carry risks of emotional dependency, manipulation, and the exploitation of vulnerable individuals. Understanding how our psyche operates in the context of séances allows for a more conscious approach to participating in them and avoiding potential negative consequences.
It is important to remember that belief in the afterlife and the desire to communicate with spirits are often rooted in natural human needs—for comfort, hope, and the search for meaning. However, this does not negate the need to critically evaluate the information received during séances. Mediums, even if they act with good intentions, may use techniques that create the illusion of communication with spirits. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a rational perspective and not let emotions completely overshadow common sense.
For those grieving a loss or seeking answers to existential questions, there are other, healthier ways to cope with difficulties. Psychological support, meditation, creative expression, or simply talking with loved ones can serve as alternatives to séances. These methods not only help process emotional experiences but also promote personal growth and strengthen mental health.
Ultimately, séances are not just mystical rituals but a reflection of deep human needs and fears. Understanding their nature allows us not only to better understand ourselves but also to make informed choices based on knowledge rather than illusions.