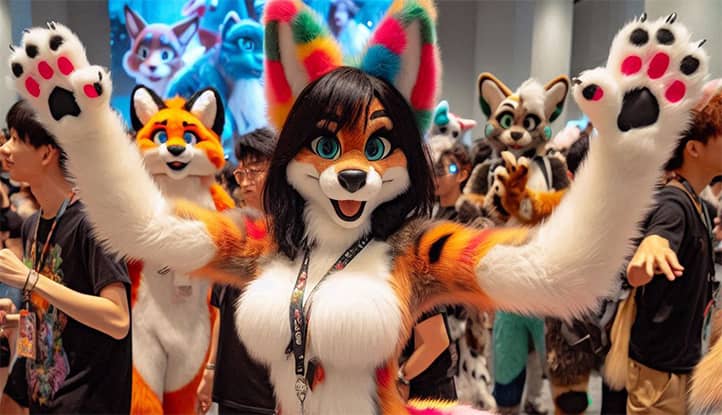
In the modern world, where the diversity of subcultures is becoming increasingly prominent, one group continues to attract particular interest and, at times, misunderstanding – the furries. Who are the furries, and why is this topic relevant to psychological analysis?
Furries are participants in a subculture fascinated by anthropomorphic animals, which are animals with human characteristics. This can manifest in creating and role-playing animal characters called “fursonas” in art, literature, role-playing games, and even in daily life through wearing costumes (fursuits).
The relevance of studying furry culture is due to several factors:
- Growing popularity. Over the past few decades, the furry community has significantly grown, attracting more participants worldwide.
- Social phenomenon. Furry culture represents a unique social phenomenon, blending elements of creativity, identity, and community.
- Psychological aspects. Studying the motivations and psychological traits of furries can shed light on broader questions of identity, self-expression, and social belonging.
- Public perception. There are many stereotypes and misconceptions about furries, making it important to conduct objective research on this subculture.
In this article, I will take a detailed look at various aspects of furry culture, focusing particularly on the psychological factors that draw people to this community and influence their behavior and self-perception.

The History of the Furry Movement
The roots of furry culture can be traced back to the mid-20th century, when anthropomorphic animals became popular characters in literature, comics, and animation. Key moments in the development of the furry movement’s precursors include:
- 1940s-1950s. The rise of anthropomorphic characters in Disney and Warner Bros. cartoons.
- 1960s-1970s. The emergence of science fiction works featuring intelligent animals, such as Arthur C. Clarke’s “2001: A Space Odyssey.”
- 1980s. The release of comic books and animated series like “Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles” and “ThunderCats,” which popularized the idea of anthropomorphic heroes.
The Development of the Community Since the 1980s
Furries began to form an organized community in the 1980s. Key stages of development include:
- 1980. The term “furry” appeared in the context of science fiction conventions.
- 1984. The creation of the first furry group at the science fiction convention Worldcon.
- 1989. The first specialized furry convention, ConFurence, held in California.
- 1990s. The spread of furry culture through the internet, with the creation of online communities and forums.
- 2000s and beyond. The global spread of furry culture, with large conventions being held around the world and the growth of social media and platforms for furry art.
Understanding the historical context is essential for psychological analysis of furry culture, as it allows us to trace the evolution of ideas and social norms within the community. It also helps explain why certain themes and imagery have become central to the furry community.

Key Aspects of Furry Culture
Furry culture, born at the intersection of fantasy and reality, represents a unique phenomenon in the modern world of subcultures. It embodies humanity’s ancient desire for unity with nature, cloaked in new, technologically mediated forms.
At the core of furry culture lies a deep human need for play and transformation. This need, retained from childhood, finds fertile ground for expression within the furry community, allowing adults to reconnect with the world of fantasy and creativity.
Anthropomorphic characters, central to furry culture, can be viewed as modern embodiments of archetypal images present in the mythology and folklore of various peoples around the world. They serve as a bridge between the human and animal aspects, allowing individuals to explore the boundaries of their own nature.
Furry art, as the visual expression of the community’s ideas, not only reflects the aesthetic preferences of its members but also serves as a mirror of social and cultural trends. Through it, we can trace the evolution of societal perceptions of beauty, individuality, and relationships between humans and the world around them.
Fursonas: Creating Anthropomorphic Characters
A fursona is a key element of furry culture, representing an anthropomorphic animal character that serves as an alter ego or an embodiment of an ideal “self” for the participant of the furry community. The psychological aspects of creating a fursona include:
- Self-expression. A fursona allows one to express aspects of their personality that may be hidden in everyday life.
- Idealization. Through their fursona, people often embody their ideal traits or desired qualities.
- Experimentation with identity. Creating a fursona can be a way to explore different aspects of one’s identity in a safe environment.
Art and Creativity in the Community
Creativity plays a central role in furry culture. It manifests in various forms:
- Visual art: Drawings, comics, 3D models of furry characters.
- Literature: Short stories, novellas, and novels with furry themes.
- Music: Creating and performing music often related to furry themes.
The psychological significance of creativity in the furry community:
- Self-actualization. The opportunity to express ideas and emotions through art.
- Social interaction. Sharing creative works as a way to establish connections within the community.
- Therapeutic effect. Creativity can serve as a form of emotional release and self-therapy.
Fursuits and Cosplay
Fursuits are costumes of anthropomorphic animals that some furries wear at conventions or other events. The psychological aspects of wearing fursuits include:
- Immersion in the role. The opportunity to fully embody one’s fursona in real life.
- Overcoming social anxiety. The costume can serve as “protection,” allowing more freedom in interacting with others.
- Playfulness. Wearing a fursuit is often perceived as a form of play, allowing one to temporarily “escape” from everyday life.
Understanding these key aspects of furry culture is important for further analysis of the psychological motivations and effects of participating in this community.

Psychological Aspects of the Furry Fandom
Immersion in the world of furries can be seen as a form of psychological adaptation to the complexities of the modern world. By creating and living through alternative identities, people find a way to cope with the pressures of social expectations and normative restrictions.
The phenomenon of furry culture is closely related to the concept of the “extended self” in psychology. A fursona becomes not just an alter ego but a tool for exploring and expanding the boundaries of one’s own personality, allowing different aspects of the self to be integrated into a more holistic image.
The interest in anthropomorphic characters may be rooted in deep layers of the psyche, connected to the archetypal images of the collective unconscious. The animal traits attributed to fursonas often symbolize certain qualities or states that a person seeks to integrate into their personality.
The process of creating and developing a fursona can be viewed as a form of narrative therapy. By constructing their character’s story, a person effectively rewrites their own story, finding new ways to interpret their experiences and overcome life challenges.
Identity and Self-expression Through a Fursona
Creating and embodying a fursona plays a significant role in the psychological aspect of furry culture. This process is closely tied to the formation and exploration of identity:
- Projection of the ideal “self”. A fursona often reflects an idealized version of the individual, embodying desired character traits or physical attributes.
- Experimentation with gender identity. Some furries use their characters to explore various gender expressions.
- Development of self-understanding. The process of creating and developing a fursona can lead to a deeper understanding of one’s own personality.
Escapism and the Creation of an Alternative Reality
The furry community is often viewed as a form of escapism, providing participants the opportunity to temporarily “escape” from reality:
- Psychological relief. Immersion in the furry world can serve as a way to relieve stress and emotional tension.
- Compensatory mechanism. For some participants, furry activities can compensate for deficiencies or difficulties in real life.
- Creative imagination. The creation of alternative worlds and scenarios stimulates the development of imagination and creativity.
Social Support and a Sense of Belonging
One of the key psychological aspects of the furry community is the strong sense of belonging and social support:
- Acceptance of diversity. The furry community is known for its openness to various forms of self-expression and identity.
- Emotional support. Many participants find in the community the understanding and support they may lack in everyday life.
- Formation of social bonds. Common interests and values foster strong friendships and romantic relationships within the community.
Understanding these psychological aspects helps explain why furry culture attracts people and the role it plays in their lives. It also allows for a better understanding of the potential benefits and risks associated with participation in the furry community.

Motivation to Participate in the Furry Community
The desire to participate in the furry community is often driven by a deep need to belong to a group of like-minded individuals. In a world where traditional forms of social connection are weakening, the furry movement offers a new model of community based on shared interests and values.
Furry culture provides a unique opportunity to experiment with different social roles and behavior models. This is especially important in the context of modern society, where traditional social institutions often struggle to adapt to rapidly changing realities.
Participation in the furry community can be seen as a form of resistance to the depersonalization and standardization characteristic of mass culture. By creating unique characters and worlds, furries affirm the value of individuality and creative self-expression.
For many participants, the furry community becomes a source of emotional support and acceptance. In a world where differences often lead to alienation, the furry community offers an environment where diversity is not only accepted but actively valued.
Creative Self-actualization
One of the main factors attracting people to furry culture is the opportunity for creative self-actualization:
- Development of artistic skills. Many furries actively engage in drawing, 3D modeling, and writing stories, which fosters the development of their creative abilities.
- A unique niche for creativity. Furry art represents a specific field where artists can experiment with forms and ideas.
- Recognition and feedback. The community provides a platform for receiving feedback and recognition for creative efforts.
Seeking Like-minded Individuals and Social Connections
Furry culture often attracts people who are seeking deep social connections:
- Shared interests. The furry community brings together people with similar hobbies, making it easier to establish contacts.
- Online and offline interaction. The opportunity to communicate both online and at conventions and meetups.
- Inclusivity. The community’s reputation for embracing diversity may attract individuals who feel isolated in other social contexts.
Exploration of One’s Identity
Participation in furry culture is often linked to the process of self-discovery and identity exploration:
- Experimentation with fursonas. Creating and “living” through different fursonas allows individuals to explore various aspects of their personality.
- Gender and sexual identity. The furry community provides a safe space for exploring gender and sexual identity.
- Development of self-confidence. Acceptance and support from the community can contribute to increased self-esteem and self-confidence.
Understanding these motivations is crucial not only for explaining the appeal of furry culture but also for debunking stereotypes and misconceptions about the community. It also helps psychologists and sociologists better understand the role of subcultures in shaping identity and social connections in modern society.

Stereotypes and Misconceptions about Furries
Stereotypes about furry culture often reflect broader social fears and prejudices. Negative perceptions of furries may be linked to a general tendency to pathologize unconventional forms of self-expression and social interaction.
The process of forming stereotypes about furries illustrates the mechanisms of social construction of reality. Media, public opinion, and individual biases create an image of the furry movement that often has little to do with reality but significantly influences the perception of this phenomenon.
The persistence of negative stereotypes about furries may be associated with cognitive dissonance. When people encounter information that contradicts their established beliefs, they tend to reject new data to maintain the integrity of their worldview.
The fight against stereotypes about furry culture represents a microcosm of the broader issue of overcoming prejudice and discrimination in society. Analyzing this process can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of forming and dismantling social stereotypes in general.
Common Myths
Furry culture often becomes the subject of various myths and misconceptions. Here are the main ones:
- “All furries are sexually attracted to animals.” This is one of the most widespread and harmful myths. In reality, most furries distinguish between their interest in anthropomorphic characters and real animals.
- “Furries are mentally ill.” There is no scientific evidence to support this claim. Participation in furry culture is not in itself a sign of mental illness.
- “All furries wear fursuits.” In fact, only a small percentage of furries own and regularly wear fursuits due to their high cost and other factors.
- “Furries are only a youth subculture.” While many participants are indeed young, the community includes people of various ages.
- “Furries can’t distinguish fantasy from reality.” Most furries are well aware of the boundary between their hobby and real life.
Reasons for the Emergence of Negative Stereotypes
Several factors contribute to the formation and spread of negative stereotypes about furries:
- Lack of information. Many people are unfamiliar with furry culture and base their opinions on rumors or distorted representations.
- Media coverage. The media often focus on the most extreme or unusual aspects of furry culture, ignoring more typical manifestations.
- Social stigmatization. Any unusual or unconventional behavior can become a target for stigmatization in society.
- Internet trolling. The anonymity of the internet facilitates the spread of negative stereotypes and exaggerated stories about furries.
- Misunderstanding of psychological aspects. Many do not understand the psychological motivations and benefits of participating in the furry community.
Impact of Stereotypes on Furries’ Psychological State
Negative stereotypes can significantly affect the psychological well-being of furry community members:
- Social isolation. The fear of stigmatization often leads furries to hide their interest, which can foster feelings of isolation.
- Stress and anxiety. Constant exposure to negative stereotypes can lead to chronic stress and heightened anxiety.
- Lower self-esteem. Negative public opinion can affect self-perception and confidence.
- Inner conflict. Some furries may experience an internal conflict between their hobby and societal expectations.
- Need for defense mechanisms. To combat negative stereotypes, furries may develop various psychological defenses, which can affect their social interactions.
Understanding and actively countering these stereotypes is important not only for improving the public perception of furry culture but also for maintaining the psychological health of its participants.

Influence of Furry Culture on Personality
Participation in furry culture can be viewed as a form of personal growth through creative self-expression. The process of creating and developing a fursona requires deep self-reflection and often leads to a better understanding of one’s desires, fears, and aspirations.
The furry movement provides a unique environment for the development of emotional intelligence. Interaction with a diverse community, where open expression of emotions is encouraged, promotes the development of empathy and emotional self-regulation skills.
Immersion in furry culture can stimulate the development of cognitive flexibility. The need to switch between different identities (real and fursona) trains adaptability and creative thinking.
The experience of participating in the furry community often leads to a reassessment of personal values and life priorities. Familiarity with alternative models of self-realization and social interaction can stimulate personal transformations and the search for new life goals.
Development of Creativity and Imagination
Participation in the furry community often contributes to the development of creative abilities:
- Stimulation of imagination. Creating fursonas and furry worlds requires active imagination.
- Development of artistic skills. Many furries engage in drawing, 3D modeling, and writing stories, which enhances their creative abilities.
- Creative problem-solving. Participation in role-playing games and creating scenarios can develop creative thinking skills.
Fostering Tolerance and Acceptance of Diversity
The furry community is known for its openness to various forms of self-expression:
- Acceptance of differences. Interaction with diverse fursonas and personalities promotes the development of tolerance.
- Broadened worldview. Familiarity with different subcultures and identities within the furry community expands one’s horizons.
- Development of empathy. Communicating with people from different backgrounds and experiences can foster the development of empathy and understanding.
Potential Risks of Over-Immersion in the Subculture
Despite many positive aspects, excessive involvement in furry culture may carry certain risks:
- Social isolation. Excessive immersion in online interactions can lead to neglect of real-life social connections.
- Blurred boundaries of reality. In rare cases, excessive identification with a fursona can make it difficult to distinguish between fantasy and reality.
- Dependence on community approval. Excessive reliance on recognition within the furry community can negatively affect self-esteem.
- Financial risks. Enthusiasm for expensive furry culture accessories (such as acquiring fursuits) can lead to financial problems.
- Neglect of other aspects of life. Over-enthusiasm can lead to neglect of work, study, or other important areas of life.
It is important to note that these risks are not inevitable or characteristic of all participants in the furry community. Many furries successfully balance their hobby with other aspects of their life. Awareness of potential risks can help community members maintain a healthy balance between their interests and everyday life.

Social Dynamics in the Furry Community
The furry community represents a unique model of social organization, combining elements of virtual and real-world interaction. This makes it an ideal laboratory for studying modern forms of sociality in the digital age.
Hierarchical structures within the furry community are often based on creative contributions and social activity rather than traditional status markers. This creates a dynamic social environment where status can change rapidly, reflecting shifts in creative activity and participant engagement.
Conflicts within the furry community often act as catalysts for the development of new forms of social interaction and dispute resolution mechanisms. The need to maintain the movement’s cohesion amid a diversity of opinions and interests encourages the development of innovative approaches to conflict management.
The phenomenon of the “furry lifestyle,” where a hobby becomes a central element of one’s life, illustrates the blurring boundaries between online and offline identities in the modern world. This creates new challenges and opportunities for personality development and social connections.
Online and Offline Interactions
The furry community is characterized by active engagement in both online and offline environments:
1. Online Platforms:
- Social networks and forums. Specialized sites like Fur Affinity, as well as general platforms like Twitter and Reddit.
- Chats and messengers. Discord servers, Telegram groups for communication and content sharing.
- Virtual worlds. Use of platforms like Second Life to create furry-oriented spaces.
Offline Events:
- Conventions. Major annual events gathering thousands of participants.
- Local meetups. Smaller, regular gatherings of local furry communities.
- Fursuit performances. Appearances in costumes at public events.
Psychological aspects of this interaction include:
- Development of social skills. Transitioning from online to offline communication can improve communicative abilities.
- Overcoming social anxiety. Gradual involvement in offline activities can help in overcoming the fear of social interaction.
- Forming deep connections. The combination of online and offline communication fosters strong friendships and romantic relationships.
Formation of Groups and Hierarchies
Despite the general atmosphere of equality, specific groups and informal hierarchies can form within the furry community:
1. Interest-based groups:
- Artists and writers;
- Fursuiters;
- Roleplayers;
- Fans of specific animal species or styles.
2. Hierarchical structures:
- Popular artists or content creators;
- Organizers of large events;
- Long-term members of the community.
Psychological aspects:
- Sense of belonging. Being part of a group can enhance the feeling of belonging to the community.
- Social status. The desire for recognition within the community can motivate skill development and active participation.
- Potential conflicts. Competition for status or resources can lead to tension between groups.
Conflict Resolution and Member Support
The furry community has developed various mechanisms for resolving conflicts and supporting its members:
1. Moderation of online platforms:
- Establishing clear behavioral rules.
- Active intervention by moderators in conflict situations.
2. Support systems:
- Mutual support groups for members facing personal issues.
- Mentorship programs for newcomers to the community.
3. Educational initiatives:
- Workshops on conflict resolution at conventions.
- Online resources for mental health and well-being.
Psychological aspects:
- Development of empathy. Active participation in conflict resolution promotes the development of empathy and understanding.
- Sense of security. The presence of support systems creates a sense of psychological safety within the community.
- Personal growth. Overcoming conflicts and supporting others can foster personal growth and the development of social skills.
Understanding the social dynamics of the furry community is important not only for its members but also for psychologists and sociologists studying modern subcultures and their influence on individuals and society at large.
Furries and Sexuality
Attitudes towards sexuality in furry culture reflect broader trends in modern society towards the deconstruction of traditional norms and taboos. The furry community’s openness to discussing and exploring various aspects of sexuality can be viewed as a form of sexual education and emancipation.
The phenomenon of “yiff” (erotic furry art and role-playing) presents an interesting subject for studying the relationship between fantasy, identity, and sexuality. It raises important questions about the nature of sexual attraction and the role of imagination in sexual experience.
The diversity of sexual and gender identities within the furry community can be seen as a microcosm of modern trends towards expanding the spectrum of recognized forms of sexuality and gender expression. This makes furry culture an important object of study for gender and sexuality researchers.
Discussions about the boundaries of acceptable sexual content within the furry community mirror broader societal debates about freedom of expression, censorship, and ethics. This makes furries an intriguing model for studying the processes of forming social norms regarding sexuality.
Diversity of Sexual Orientations in the Community
The furry community is known for its openness to various sexual orientations and gender identities:
- Statistics. Research shows that the percentage of LGBTQ+ identifications within the furry community is higher compared to the general population.
- Acceptance of diversity. The community actively supports the acceptance of various sexual orientations and gender identities.
- Self-exploration. Many members of the community note that furry culture provided them with a safe space to explore their sexuality and gender identity.
Psychological aspects:
- Identity formation. An open environment can contribute to more freely forming and accepting one’s sexual identity.
- Reduction of minority stress. An accepting atmosphere can reduce the stress associated with being part of a sexual minority.
The Role of Furries in Sexual Exploration
Furry culture often provides a unique space for exploring sexuality:
- Fursonas and gender expression. Creating a fursona allows individuals to experiment with different gender expressions and sexual identities in a safe environment.
- Role-playing. Online role-playing games and text-based interactions allow for the exploration of various scenarios and relationships.
- Artistic expression. Furry art often includes erotic elements, enabling the expression and exploration of sexual fantasies.
Psychological aspects:
- Self-discovery. Experimenting with identities can lead to a better understanding of one’s own preferences and desires.
- Reduction of anxiety. A safe space for exploring sexuality can reduce anxiety associated with sexual expression.
Separating the Sexual Aspect from Furry Culture as a Whole
It is important to note that sexuality is not a central aspect of furry culture for all its members:
- Variety of motivations. Many furries participate in the community due to an interest in art, cosplay, or social interaction, without any sexual connotations.
- SFW (Safe For Work) content. The majority of furry content does not contain sexual elements and is suitable for general viewing.
- Separation of spaces. Many online platforms and offline events clearly distinguish between adult content and general content.
Psychological aspects:
- Balancing identities. The ability to separate sexual and non-sexual aspects of the hobby contributes to healthy psychological functioning.
- Reducing stigmatization. Emphasizing non-sexual aspects of furry culture helps combat negative stereotypes.
- Inclusivity. Separating sexual and non-sexual content makes the community more accessible to people of all ages and preferences.
It is important to emphasize that attitudes towards sexuality in the furry movement reflect general societal trends toward greater openness and acceptance of diversity. At the same time, as in any other subculture, there are individual differences in attitudes towards sexuality and its role in personal identification with furry culture.

Therapeutic Potential of Furry Culture
Creating and embodying a fursona can be seen as a form of self-therapy, allowing individuals to explore and integrate various aspects of their personality in a safe and controlled environment. This process has parallels with techniques used in drama therapy and psychodrama in professional therapeutic practice.
Participation in the furry community can serve as a buffer against social isolation and loneliness, particularly for people who struggle with social interaction in traditional contexts. The sense of belonging and acceptance typical of furry culture can have a significant positive effect on psychological well-being.
Creative aspects of furry culture, such as drawing or writing stories, can be seen as a form of art therapy. These activities allow individuals to express and process emotions and experiences that are difficult to verbalize.
Fursuiting (wearing furry character costumes) has a therapeutic effect similar to embodied cognition techniques in psychotherapy. Physically embodying an alternative identity can contribute to changes in thought and behavior patterns, helping to overcome psychological barriers and limitations.
Overcoming Social Anxiety
Participation in the furry community can play a significant role in overcoming social anxiety:
- Gradual immersion. Online interactions allow for a gradual adjustment to social contact.
- Using a fursona. Communicating through a fursona reduces anxiety related to self-presentation.
- Supportive environment. The accepting atmosphere of the community fosters confidence in social situations.
Psychological Mechanisms:
- Desensitization. Gradual increase in social contacts reduces sensitivity to social stressors.
- Cognitive restructuring. Positive experiences of communication help change negative beliefs about social interactions.
Increasing self-esteem and confidence
Furry culture contributes to increased self-esteem and confidence:
- Creative self-expression. Creating and developing a fursona can be a source of pride and satisfaction.
- Positive feedback. Recognition of creativity and personality within the community strengthens self-worth.
- Acceptance of uniqueness. A culture that values individuality helps individuals accept and embrace their traits.
Psychological Effects:
- Development of positive self-identification. Creating a positive self-image through a fursona can extend to overall self-perception.
- Increased self-efficacy. Successes in creativity or social interactions within the community can enhance belief in one’s abilities.
Opportunities for Self-Exploration and Personal Growth
Participation in furry culture provides unique opportunities for self-exploration and personal growth:
- Experimenting with identity. Creating and embodying different fursonas helps in exploring various aspects of personality.
- Developing empathy. Interaction with a diverse community fosters understanding and acceptance of others.
- Overcoming personal boundaries. Participation in conventions and events allows individuals to step out of their comfort zones and develop new skills.
Psychological Processes:
- Self-actualization. The opportunity for free self-expression helps realize personal potential.
- Integration of personality. Exploring different aspects of oneself through fursonas contributes to the formation of a more cohesive personality.
It is important to note that while furry culture may have therapeutic effects, it does not replace professional psychological help. Individuals facing serious psychological issues should seek qualified specialists.
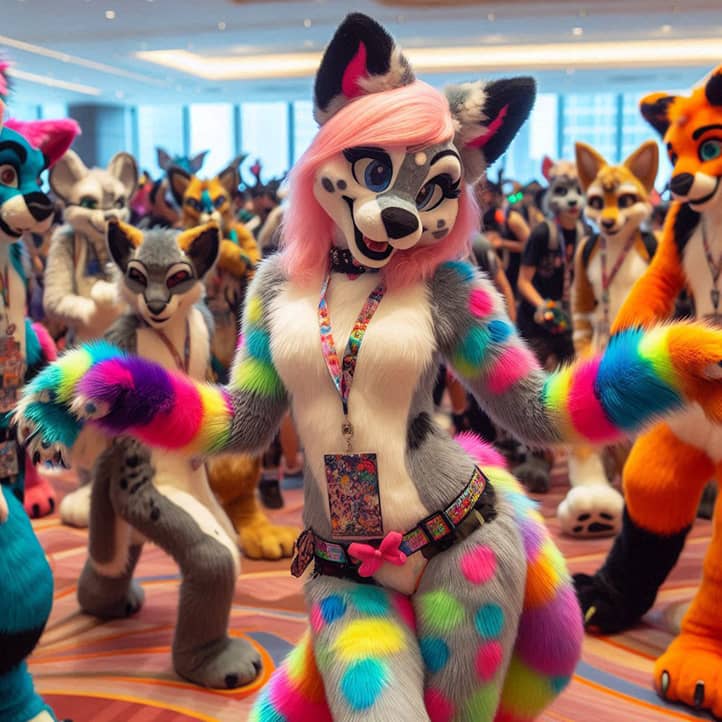

Conclusion
Furry culture represents a multifaceted phenomenon that reflects complex processes of identity formation and social interactions in the modern world. It serves as a unique space for self-expression, creativity, and exploration of various aspects of human psychology.
The psychological aspects of participating in the furry community range from personal growth and increased self-esteem to overcoming social anxiety and developing empathy. Furry culture provides a safe environment for experimenting with identity and social roles, which can have significant therapeutic effects.
However, like any social phenomenon, furry culture is not free from internal contradictions and external stereotypes. Negative societal perceptions and stigmatization can significantly impact the psychological well-being of community members. This underscores the importance of further study and understanding of this phenomenon.
Future research on furry culture may shed light on many aspects of modern psychology and sociology. It could help better understand the processes of identity formation in the digital age, mechanisms of social adaptation, and the role of creative self-expression in psychological well-being. Additionally, studying the furry community could provide valuable insights for developing new approaches in psychotherapy and social work.
Ultimately, the phenomenon of furry culture reminds us of the importance of embracing the diversity of human experience and the potential for self-expression through fantasy and creativity. It demonstrates how people can find communication, support, and self-identification beyond traditional roles and images. Furry culture teaches us to value individuality and embrace unconventional forms of self-expression, which can unite people despite their differences through a shared desire for creative exploration of self and the world.




