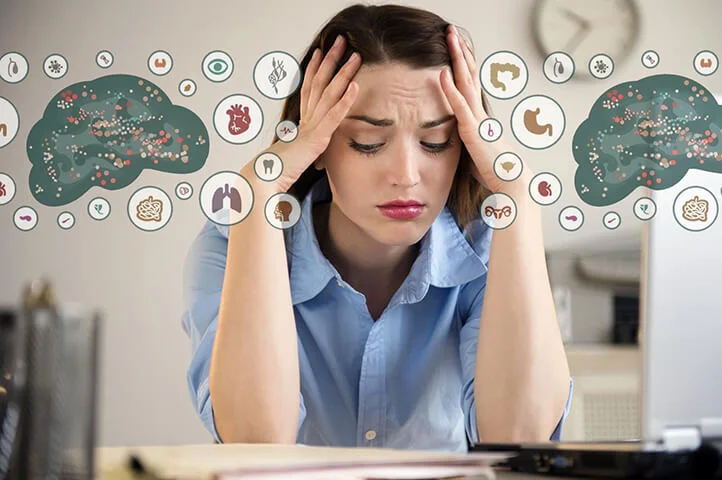
Psychosomatic illnesses refer to physical ailments that arise or worsen under the influence of psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, depression, and other emotional disturbances. This concept is based on the close connection between the mind (psyche) and the body (soma), which exists in the human organism.
For many years, psychosomatic disorders have been the subject of debate and discussion in the medical community. However, their existence is now widely recognized, and increasing attention is being paid to studying the mechanisms underlying these illnesses, as well as developing effective treatment methods.
The idea that emotions and psychological factors can affect physical health existed in ancient civilizations. However, the scientific study of psychosomatic illnesses began only in the late 19th century, when doctors started noticing the link between patients’ psychological states and certain physical symptoms.
In the 1920s, German psychoanalyst Franz Alexander and his colleagues proposed the concept of the “specific neurotic personality,” according to which certain personality types and characteristics predispose individuals to the development of specific psychosomatic disorders.
In the following decades, research in this area continued, and over time, scientists have come to better understand the role of stress, emotions, and other psychological factors in the development of various diseases.
Studying psychosomatic illnesses is of great importance to modern medicine and healthcare. Understanding the mechanisms underlying these disorders allows for the development of more effective treatment methods, combining medication therapy with psychological support.
Moreover, acknowledging the role of psychological factors in the development of physical illnesses contributes to changing the approach to the prevention and treatment of many diseases. Increasing attention is being given to stress management, relaxation techniques, and other methods to improve psychological well-being.
Mechanisms of Psychosomatic Illnesses
Understanding the mechanisms underlying psychosomatic illnesses is a key aspect of their study. Although research in this area is ongoing, scientists have identified several major pathways through which psychological factors can affect a person’s physical health.
The Role of Stress and Emotional Tension
One of the most important factors contributing to the development of psychosomatic illnesses is stress. Prolonged exposure to stress triggers complex biochemical and physiological changes in the body, which can negatively affect the functioning of various systems and organs.
Chronic stress leads to an increase in the levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause:
- Increased blood pressure
- Metabolic disturbances
- Weakened immune system
- Heightened inflammatory processes in the body
In addition, stress is often accompanied by unhealthy habits such as smoking, alcohol consumption, irregular eating, and lack of physical activity, which further negatively impact health.
The Influence of Psychological Factors
Apart from stress, there are several other psychological factors that contribute to the development of psychosomatic illnesses. These include:
- Anxiety and depression: These conditions are associated with changes in the brain’s neurochemical processes, which can affect various physiological functions in the body.
- Suppressed emotions: The inability to express and cope with strong emotions such as anger, fear, or grief can lead to chronic nervous tension and negative physical consequences.
- Negative thought patterns: A pessimistic outlook on life, catastrophizing situations, and other unhealthy cognitive patterns can contribute to the development of psychosomatic symptoms.
Dysregulation of the Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) plays a key role in regulating many physiological processes in the body, such as cardiac activity, breathing, digestion, and others. Stress and emotional disturbances can lead to an imbalance in the ANS, which in turn can contribute to the development of various diseases.
For example, chronic stress can lead to increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system (responsible for the “fight or flight” response), which can negatively affect the cardiovascular and digestive systems.
The Impact of Lifestyle and Behavioral Factors
Psychological factors can also influence lifestyle choices and behavioral habits, which, in turn, affect physical health. People experiencing chronic stress or emotional disturbances are more likely to resort to unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as:
- Alcohol abuse and smoking
- Unhealthy eating habits (overeating, fast food, high-calorie foods)
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Sleep disorders
These behavioral factors contribute to the development of various illnesses, such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular and respiratory diseases.
Examples of Psychosomatic Diseases
Psychosomatic illnesses can affect various systems and organs of the human body. Their symptoms are often physical in nature, but their onset and exacerbation are closely related to psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, depression, and suppressed emotions.
One of the most common groups of psychosomatic illnesses is disorders related to the gastrointestinal tract. Psychological factors can affect the secretion of gastric acid, bowel motility, and contribute to inflammatory processes in the digestive system.
Another important category of psychosomatic diseases is cardiovascular disorders. In this case, stress, anger, and depression can negatively impact heart and vascular function, increasing the risk of conditions such as hypertension and coronary heart disease.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Peptic ulcer disease of the stomach and duodenum: Stress and anxiety are among the major risk factors for developing peptic ulcers, as they provoke increased acidity of gastric juice and damage to the mucosal lining.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): This functional disorder is characterized by chronic abdominal pain, bloating, and bowel irregularities. It is believed that stress and psychological factors play a significant role in the development and exacerbation of IBS.
- Functional dyspepsia: Chronic pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, bloating, heartburn, and other symptoms may be linked to psychological stress and impaired digestive function.
Cardiovascular Diseases
- Hypertension (high blood pressure): Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression are risk factors for the development of hypertension, as they contribute to elevated blood pressure and vascular tone dysregulation.
- Coronary heart disease (CHD): Psychosomatic factors such as stress, anger, and depression can increase the risk of developing CHD, including myocardial infarction and angina. They negatively affect the cardiovascular system by increasing inflammation and disrupting lipid metabolism.
Respiratory Diseases
- Bronchial asthma: Stress and emotional factors are among the main triggers for asthma attacks. They can cause bronchial spasms.
- Respiratory hypersensitivity: Chronic tension and anxiety can contribute to airway hyperreactivity, manifesting as cough, shortness of breath, and other respiratory symptoms.
Skin Diseases
- Eczema: This chronic inflammatory skin disease is often linked to psychological stress and emotional disturbances. Stress can exacerbate itching, dryness, and skin rashes.
- Psoriasis: This autoimmune skin disease can flare up under stress and negative emotions. Stress often disrupts immune system function and promotes inflammatory processes in the body.
- Neurodermatitis: Chronic stress can be a triggering factor for neurodermatitis flare-ups—a condition characterized by itching, dry skin, and rashes.
Chronic Pain
- Headaches and migraines: Stress, anxiety, and depression are among the major risk factors for developing these conditions. They can contribute to increased muscle tension and dysregulation of vascular tone in the brain.
- Fibromyalgia: This chronic condition is characterized by pain in muscles and connective tissues. Psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and depression may play a role in the development and exacerbation of fibromyalgia by affecting pain perception and stress hormone regulation.

How Are Psychosomatic Diseases Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of psychosomatic diseases is a complex task requiring a comprehensive approach. Since these conditions manifest through physical symptoms, it is essential to carefully rule out organic causes before assuming a psychosomatic nature of the illness.
The diagnostic process for psychosomatic illnesses begins with taking the patient’s medical history, complaints, and conducting a physical examination. Then, the doctor prescribes necessary laboratory and instrumental tests, such as blood tests, X-rays, ultrasounds, ECGs, and others, to rule out serious organic diseases that could cause similar symptoms.
Only after thoroughly ruling out organic causes can a psychological evaluation of the patient be conducted.
Exclusion of Organic Causes
At the stage of excluding organic causes, it is important to conduct all necessary tests and diagnostic procedures to ensure the absence of serious illnesses such as:
- Tumor processes
- Autoimmune diseases
- Infections
- Endocrine disorders
- Injuries and trauma
The doctor must be very attentive and correctly interpret the examination results to avoid missing possible organic causes of the symptoms.
Psychological Assessment
After ruling out organic causes, the next step is to assess the patient’s psychological state. This can involve the following methods:
- Clinical interviews and questionnaires to identify stress factors, emotional disturbances, personality traits, and coping strategies.
- Psychological testing to assess levels of anxiety, depression, stress, and other psychological indicators.
- Consultation with a psychologist or psychotherapist for a deeper assessment of the mental state.
Use of Special Psychodiagnostic Techniques
In some cases, special psychodiagnostic techniques may be used to diagnose psychosomatic illnesses, such as:
- Projective tests (Rorschach Inkblot Test, Thematic Apperception Test, etc.)
- Personality assessment tools (MMPI, 16PF, Cattell’s test, etc.)
- Specialized questionnaires to assess psychosomatic disorders.
These techniques help to gain deeper insights into the patient’s personality traits, emotional state, and unconscious processes, which can be useful for diagnosis and treatment selection.
It is important to understand that the diagnosis of psychosomatic diseases is a complex, multi-stage process that requires close cooperation between physicians from various specialties and psychologists. Only a comprehensive approach, considering both physical and psychological factors, can ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.

Treatment and Prevention of Psychosomatic Diseases
The approach to treating psychosomatic diseases should be comprehensive and take into account both physical symptoms and psychological factors that contribute to their development and exacerbation. Ignoring one of these aspects may lead to ineffective therapy and relapses.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to address physical symptoms. However, it is essential to understand that medications only relieve the condition but do not eliminate the root cause of the disease, which often lies in psychological factors. Therefore, medication therapy should be combined with psychotherapeutic methods.
Psychotherapy plays a crucial role in the treatment of psychosomatic diseases, helping patients cope with psychological issues such as stress, anxiety, depression, and unhealthy patterns of thinking and behavior. The most effective psychotherapy methods include cognitive-behavioral therapy, relaxation techniques, group therapy, and family therapy.
Medication Therapy
For some psychosomatic diseases, medication may be required to relieve physical symptoms. The choice of drugs depends on the specific disease and its manifestations. For example:
- To treat peptic ulcers and gastritis, antacid medications, proton pump inhibitors may be used.
- In the case of bronchial asthma, bronchodilators and inhaled glucocorticosteroids are commonly prescribed.
- For depression and anxiety disorders, antidepressants and anxiolytics may be recommended.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy plays a key role in treating psychosomatic disorders by helping patients cope with psychological factors contributing to symptom development and exacerbation. The most effective psychotherapy methods include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): Focuses on identifying and changing unhealthy patterns of thinking and behavior that contribute to symptom development.
- Relaxation techniques: Methods such as progressive muscle relaxation, meditation and yoga help reduce stress and anxiety levels.
- Group psychotherapy: Allows patients to gain support and share experiences with people facing similar problems.
- Family therapy: Helps resolve family conflicts and improve communication, reducing stress levels.
Lifestyle Changes and Stress Management
Lifestyle changes and mastering stress management techniques play a significant role in treating and preventing psychosomatic diseases. Recommended measures include:
- Balanced nutrition: A healthy, nutrient-rich diet is essential for maintaining overall health and increasing the body’s stress resilience.
- Regular physical activity: Exercise helps reduce stress, improves mood, and enhances overall well-being.
- Adequate sleep: Sleep disturbances can worsen the symptoms of psychosomatic disorders, so maintaining a healthy sleep routine is crucial.
- Avoiding bad habits: Smoking, alcohol abuse, and other unhealthy habits negatively affect health and can worsen symptoms.
- Stress management techniques: Learning relaxation techniques, meditation, yoga, breathing exercises, and other stress-reduction methods.
The Importance of a Comprehensive Approach
For optimal results in treating psychosomatic disorders, a comprehensive approach is needed, combining medication therapy (if necessary), psychotherapy, lifestyle changes, and stress management techniques. This multifaceted approach addresses both physical symptoms and eliminates the psychological causes contributing to the development and exacerbation of diseases.
It is also important to understand that treating psychosomatic disorders requires patience, as changes may occur gradually. Regular interactions with doctors and psychologists, following recommendations, and the patient’s active involvement in the treatment process are key success factors.
Psychoeducational Programs and Increasing Psychological Literacy
In addition to medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes, psychoeducational programs and increasing psychological literacy among the population play a vital role in treating and preventing psychosomatic disorders.
Psychoeducational programs aim to educate patients and their families about the mechanisms behind the development of psychosomatic diseases, the role of psychological factors, and how to cope with stress and emotional disturbances. These programs can be delivered through lectures, seminars, training sessions, or individual consultations.
Increasing psychological literacy among the general population is also important. People should recognize the importance of mental health, be able to identify symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression, and know where to seek help when psychological problems arise.
Psychoeducational programs and mental health awareness contribute to:
- Early detection and timely treatment of psychosomatic disorders.
- Increased motivation for treatment and adherence to the recommendations of doctors and psychologists.
- Reducing the stigma around psychosomatic and mental illnesses.
- Preventing the development of psychosomatic diseases by teaching self-regulation of emotional states and stress management skills.
Thus, psychoeducation and increasing psychological literacy are important components of a comprehensive approach to treating and preventing psychosomatic disorders, complementing medication therapy, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes.
The Role of Psychosocial Support and Rehabilitation
Psychosocial support and rehabilitation play a crucial role in restoring and maintaining the mental and physical health of patients with psychosomatic disorders.
Psychosocial support involves creating an environment where the patient feels accepted, understood, and receives the necessary emotional and practical help. This can be provided through:
- Group psychotherapy and support groups, where patients can share experiences and support each other.
- Family therapy aimed at improving relationships and communication within the family.
- Social support from close ones, friends, and specialists (such as social workers, nurses, etc.).
Rehabilitation for patients with psychosomatic diseases focuses on restoring their ability to function in daily life, work, and society. It may include:
- Professional rehabilitation and employment assistance.
- Training in independent living skills and self-care.
- Physical rehabilitation to restore physical functions.
- Psychological rehabilitation to develop coping strategies and strengthen mental health.
Psychosocial support and rehabilitation are integral parts of the comprehensive approach to treating psychosomatic diseases. They help patients cope with the psychological and social consequences of illness, improve their quality of life, and facilitate successful reintegration into society.
It should be noted that psychosocial support and rehabilitation should be individualized, considering the needs and characteristics of each patient. An effective rehabilitation program requires close cooperation between healthcare professionals, psychologists, social workers, and other specialists.
Conclusion
Psychosomatic diseases vividly illustrate the close connection between mind and body. Ignoring this connection can lead to severe consequences for a person’s health. Understanding the mechanisms underlying psychosomatic disorders is of great importance for modern medicine and healthcare.
The study of psychosomatic diseases clearly demonstrates that the mind and body are not separate components of the human being but are an interconnected system. Psychological factors, such as stress, anxiety, depression, and repressed emotions, can significantly affect physical health, contributing to the development or worsening of various diseases.
Recognizing this connection is crucial for changing the approach to preventing and treating many ailments. Increasing attention is being paid not only to physical symptoms but also to the patient’s psychological state and the factors influencing their emotional well-being.
Despite growing recognition of psychosomatic disorders, many people remain insufficiently informed about this issue. It is essential to raise awareness about psychosomatic diseases, their symptoms, and risk factors so that people can recognize the problem early and seek help.
It is also important to combat the stigma surrounding psychosomatic diseases and explain that they are not “imaginary” or “made-up” problems but real illnesses requiring comprehensive treatment.
To prevent the development of psychosomatic disorders and maintain health, it is essential to:
- Learn to manage stress effectively using various methods such as relaxation techniques, meditation, yoga, etc.
- Monitor emotional well-being and seek help from specialists (psychologists, psychotherapists) when experiencing anxiety or depressive symptoms.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, sufficient sleep, and avoiding harmful habits.
- Seek medical attention for physical symptoms, not dismissing them as merely stress or fatigue.
Early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment of psychosomatic diseases are crucial for preventing serious complications and restoring health.
In conclusion, it is important to emphasize that caring for mental health is just as important as caring for physical well-being. Understanding the connection between mind and body, raising awareness of psychosomatic disorders, and seeking timely help from professionals can significantly improve the quality of life for anyone.